Babel API

参考
- https://www.babeljs.cn/docs/babel-parser
- https://juejin.cn/book/6946117847848321055/section/6946578914764390434?enter_from=course_center&utm_source=course_center#heading-1 (需要付费)
- babel github https://github.com/babel/babel
我们知道 babel 的编译流程分为三步:parse、transform、generate,每一步都暴露了一些 api 出来。
-
parse阶段有@babel/parser,功能是把源码转成 AST -
transform阶段有@babel/traverse,可以遍历 AST,并调用visitor函数修改 AST,- 修改 AST 自然涉及到 AST 的判断、创建、修改等,这时候就需要
@babel/types了 - 当需要批量创建 AST 的时候可以使用
@babel/template来简化 AST 创建逻辑。
- 修改 AST 自然涉及到 AST 的判断、创建、修改等,这时候就需要
-
generate阶段会把 AST 打印为目标代码字符串,同时生成sourcemap,需要@babel/generator包 -
中途遇到错误想打印代码位置的时候,使用
@babel/code-frame包 -
babel的整体功能通过@babel/core提供,基于上面的包完成 babel 整体的编译流程,并应用 plugin 和 preset。
主要学习的就是
-
@babel/parser -
@babel/traverse -
@babel/generator -
@babel/types -
@babel/template
这五个包的 api 的使用。
这些包的 api 都可以在文档里查看:
@babel/parser
下面的介绍都可以在官方文档中看到
Babel 分析器(前身为 Babylon)是 Babel 中使用的 JavaScript 分析器。
默认启用最新的 ECMAScript 版本(ES2020)。
支持 JSX、Flow 和 Typescript。
支持实验性语言提案(接受任何至少stage-0的 PR)。
它提供了有两个 api:
-
babelParser.parse(code, [options])parse()将提供的代码作为整个 ECMAScript 程序进行解析
-
babelParser.parseExpression(code, [options])parseExpression()返回的 AST 根节点是是 Expression(表达式的 AST),粒度不同。
详细的 options 可以查看文档。其实主要分为两类,一是 parse 的内容是什么,二是以什么方式去 parse
parse 的内容是什么:
-
plugins: 指定jsx、typescript、flow 等插件来解析对应的语法 -
allowXxx: 指定一些语法是否允许,比如函数外的 await、没声明的 export等 -
sourceType: 指定是否支持解析模块语法,有 module、script、unambiguous 3个取值:module:解析es module语法script:不解析es module语法unambiguous:根据内容是否有import和export来自动设置module还是script
const parser = require('@babel/parser')
const code = `interface Shape {
name: string;
width: number;
height: number;
color?: string;
}
function area(shape : Shape) {
var area = shape.width * shape.height;
return "I'm " + shape.name + " with area " + area + " cm squared";
}
console.log( area( {name: "rectangle", width: 30, height: 15} ) );`
const ast = parser.parse("code", {
sourceType: 'unambiguous',
plugins: ['typescript']
});
console.log(JSON.stringify(ast))
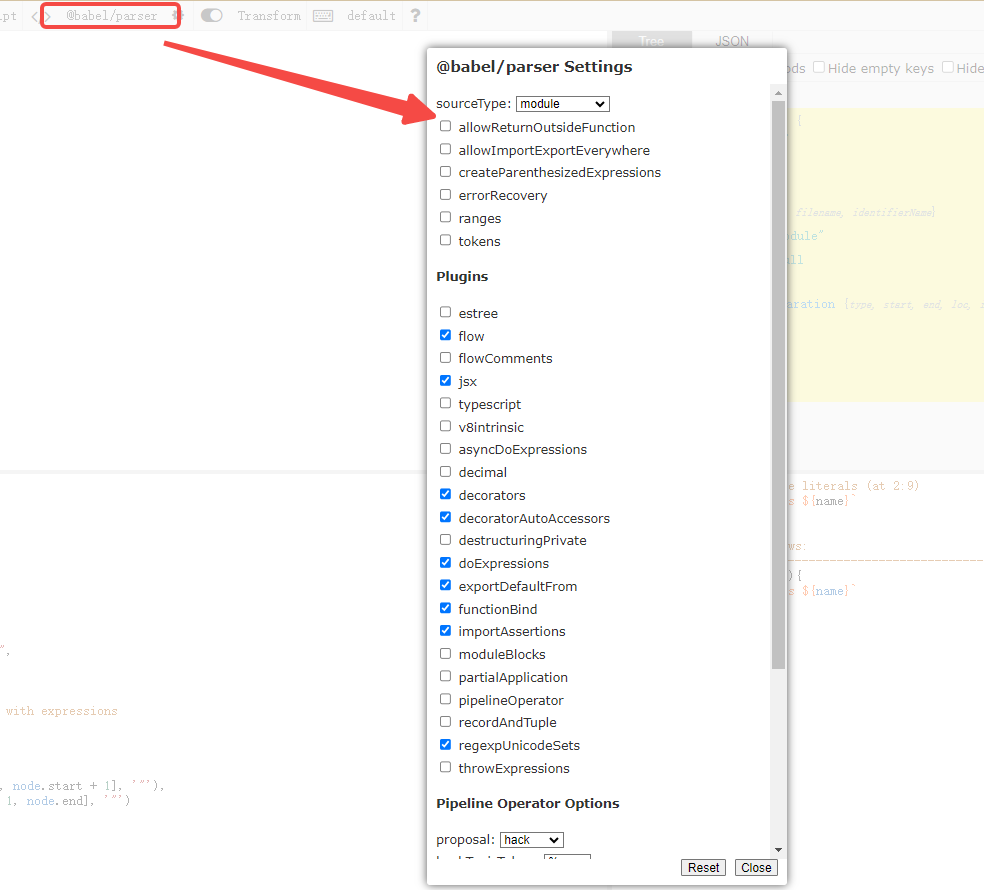
当你使用在线astexplorer的时候,这里也同样支持 parser options 的设置
@babel/traverse
文档地址:https://www.babeljs.cn/docs/babel-traverse
parse 出的 AST 由 @babel/traverse 来遍历和修改,babel traverse 包提供了 traverse 方法:
traverse 方法
下面是 traverse 方法的类型声明
declare const traverse: {
<S>(parent: Node, opts: TraverseOptions<S>, scope: Scope | undefined, state: S, parentPath?: NodePath): void;
(parent: Node, opts?: TraverseOptions, scope?: Scope, state?: any, parentPath?: NodePath): void;
visitors: typeof visitors;
verify: typeof visitors.verify;
explode: typeof visitors.explode;
cheap: (node: Node, enter: (node: Node) => void) => void;
node: (
node: Node,
opts: TraverseOptions,
scope?: Scope,
state?: any,
path?: NodePath,
skipKeys?: Record<string, boolean>,
) => void;
clearNode: (node: Node, opts?: RemovePropertiesOptions) => void;
removeProperties: (tree: Node, opts?: RemovePropertiesOptions) => Node;
hasType: (tree: Node, type: Node["type"], denylistTypes?: string[]) => boolean;
cache: typeof cache;
};
前面两个参数是比较常用的,parent 指定要遍历的 AST 节点,opts 指定 visitor 函数。babel 会在遍历 parent 对应的 AST 时调用相应的 visitor 函数。
visitor 函数
export interface VisitNodeObject<S, P extends Node> {
enter?: VisitNodeFunction<S, P>; // 进入节点执行
exit?: VisitNodeFunction<S, P>; // 离开节点执行
}
traverse(ast, {
enter(path) {
console.log('enter')
},
exit(path) {
console.log('exit')
},
})
$ node app.js
enter
enter
enter
exit
exit
exit
这里我们输出遍历节点的type会更清晰
traverse(ast, {
enter(path) {
console.log('enter',path.type)
},
exit(path) {
console.log('exit',path.type)
},
})
$ node app.js
enter Program
enter ExpressionStatement
enter Identifier
exit Identifier
exit ExpressionStatement
exit Program
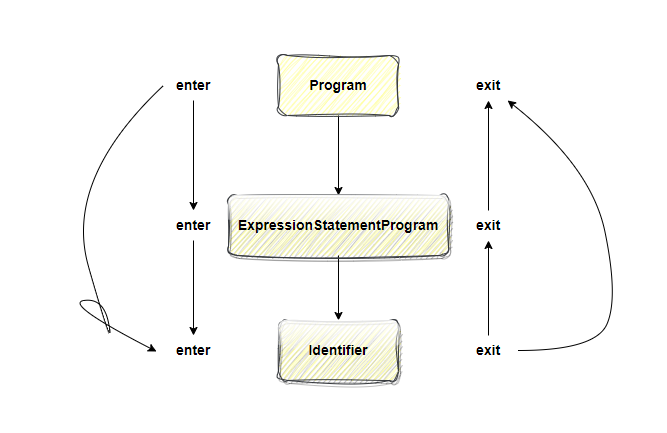
基本可以看出很像一个栈数据结构的感觉,先进后出
先从最外面的节点
Program enter然后
enter内部子节点ExpressionStatement继续
enter到最内层的Identifier,然后在反向
exit先退出Identifier,然后
exitExpressionStatement最后
exitProgram
此外,我们可以针对语法树中的特定节点类型,比如下面是针对 Program 节点的
traverse(ast, {
Program: {
enter(path) {
console.log('enter', path.type)
},
exit(path) {
console.log('exit', path.type)
},
},
})
$ node app.js
enter Program
exit Program
可以看到其他只进行了 Program 节点的遍历
如果只存在一个函数的话,那么默认就是 enter 阶段的调用
traverse(ast, {
Program(path) {}
})
这里可以从源码中看到https://github.com/babel/babel/blob/main/packages/babel-types/src/traverse/traverse.ts
enter 时调用是在**遍历当前节点的子节点** 前 调用,exit 时调用是**遍历完当前节点的子节点** 后 调用。
visitor 函数的参数 - path
AST 是棵树,遍历过程中肯定是有个路径的,path 就记录了这个路径
在整个过程中,祖先信息(包括父节点、父节点的键以及父节点的索引)被保存在一个ancestors数组中,并传递给每个处理程序。这个就是path 记录了遍历过的所有节点!
// 定义TraversalAncestors类型,用于存储祖先信息
export type TraversalAncestors = Array<{
node: t.Node; // 祖先节点
key: string; // 祖先节点的键
index?: number; // 如果祖先节点是数组类型,那么这个字段表示当前节点在数组中的索引
}>;
// 定义TraversalHandler类型,用于描述一个处理程序
export type TraversalHandler<T> = (
this: undefined,
node: t.Node, // 当前节点
parent: TraversalAncestors, // 祖先信息
state: T, // 用户提供的状态对象
) => void;
// 定义TraversalHandlers类型,用于描述一组处理程序
export type TraversalHandlers<T> = {
enter?: TraversalHandler<T>; // 预处理程序
exit?: TraversalHandler<T>; // 后处理程序
};
// 实现一个通用的AST遍历器
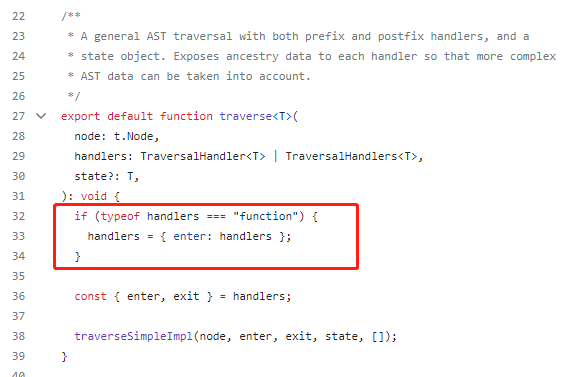
export default function traverse<T>(
node: t.Node, // 要遍历的节点
handlers: TraversalHandler<T> | TraversalHandlers<T>, // 处理程序或者一组处理程序
state?: T, // 用户提供的状态对象
): void {
if (typeof handlers === "function") {
handlers = { enter: handlers }; // 如果handlers只是一个函数,则将其转化为{ enter: handlers }
}
const { enter, exit } = handlers; // 获取处理程序
traverseSimpleImpl(node, enter, exit, state, []); // 调用内部函数进行实际的遍历操作
}
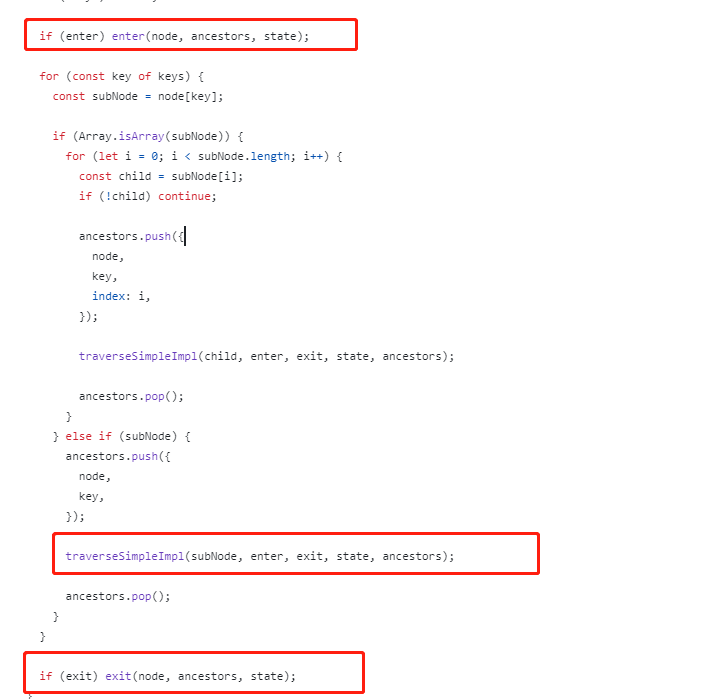
function traverseSimpleImpl<T>(
node: any, // 当前节点
enter: Function | undefined, // 预处理程序
exit: Function | undefined, // 后处理程序
state: T | undefined, // 用户提供的状态对象
ancestors: TraversalAncestors, // 祖先信息
) {
const keys = VISITOR_KEYS[node.type]; // 获取当前节点类型的所有子节点键名
if (!keys) return; // 如果没有子节点键名,则直接返回
if (enter) enter(node, ancestors, state); // 如果有预处理程序,则调用预处理程序
for (const key of keys) { // 对每个子节点键进行遍历
const subNode = node[key];
if (Array.isArray(subNode)) { // 如果子节点是数组类型
for (let i = 0; i < subNode.length; i++) { // 遍历数组中的每个元素
const child = subNode[i];
if (!child) continue; // 如果元素为null或undefined,则跳过
ancestors.push({ // 将祖先信息推入栈顶
node,
key,
index: i,
});
traverseSimpleImpl(child, enter, exit, state, ancestors); // 递归地遍历元素
ancestors.pop(); // 弹出栈顶的祖先信息
}
} else if (subNode) { // 如果子节点是非数组类型
ancestors.push({ // 将祖先信息推入栈顶
node,
key,
});
traverseSimpleImpl(subNode, enter, exit, state, ancestors); // 递归地遍历子节点
ancestors.pop(); // 弹出栈顶的祖先信息
}
}
if (exit) exit(node, ancestors, state); // 如果有后处理程序,则调用后处理程序
}
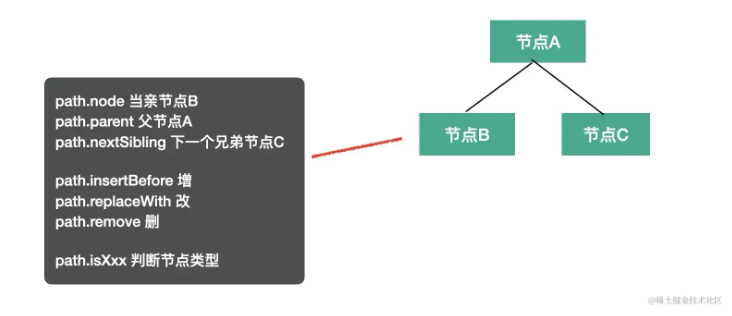
path 有很多属性和方法,比如记录父子、兄弟等关系的:
path.node指向当前 AST 节点path.parent指向父级 AST 节点path.getSibling、path.getNextSibling、path.getPrevSibling获取兄弟节点path.find从当前节点向上查找节点path.get、path.set获取 / 设置属性的 path
还有作用域相关的:
path.scope获取当前节点的作用域信息
判断 AST 类型的:
path.isXxx判断当前节点是不是 xx 类型path.assertXxx判断当前节点是不是xx类型,不是则抛出异常
增删改 AST 的:
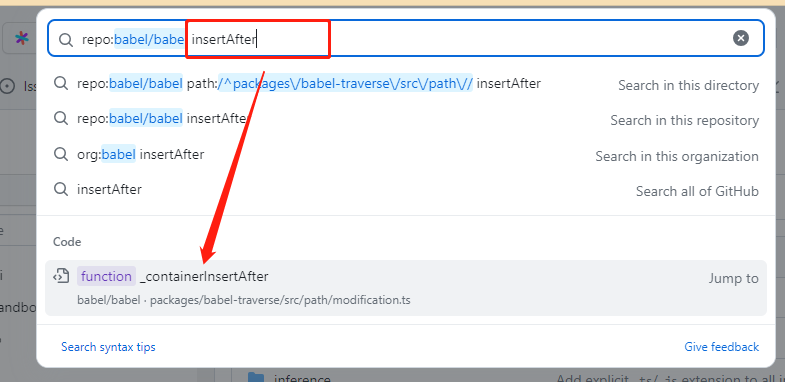
path.insertBefore、path.insertAfter插入节点path.replaceWith、path.replaceWithMultiple、replaceWithSourceString替换节点path.remove删除节点
跳过遍历的:
path.skip跳过当前节点的子节点的遍历path.stop结束后续遍历
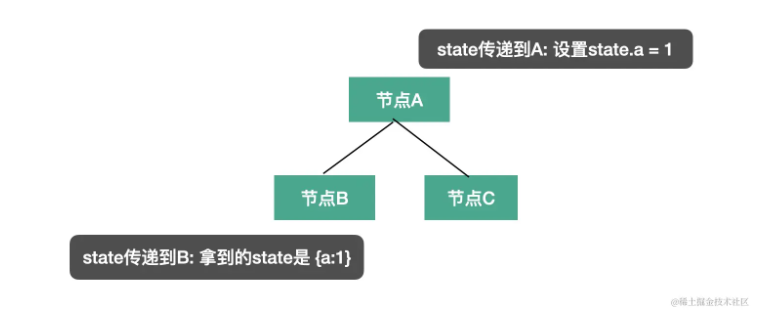
visitor 函数的参数 - state
这个很容易理解,节点之间是有传输数据的需求的。不同状态下可能会做不同的处理,这就是为什么这个参数叫做 state。
源码中是有递归传递state的,并且为 enter or exit 的回调参数
插件会通过 state 传递 options 和 file 信息,我们也可以通过 state 存储一些遍历过程中的共享数据。
@babel/types
This module contains methods for building ASTs manually and for checking the types of AST nodes.
该模块包含手动构建 AST 和检查 AST 节点类型的方法。
举例来说,如果要创建IfStatement就可以调用
t.ifStatement(test, consequent, alternate);
而判断节点是否是 IfStatement 就可以调用 isIfStatement 或者 assertIfStatement
t.isIfStatement(node, opts);
t.assertIfStatement(node, opts);
opts 可以指定一些属性是什么值,增加更多限制条件,做更精确的判断。
t.isIdentifier(node, { name: "paths" })
isXxx 和 assertXxx 看起来很像,但是功能不大一样:isXxx 会返回 boolean,而 assertXxx 则会在类型不一致时抛异常。
所有的 AST 的 build、assert 的 api 可以在 babel types 文档中查。
@babel/template
提供了代码直接创建为AST树的能力
通过上面@babel/types 创建 AST 还是比较麻烦的,要一个个的创建然后组装,如果 AST 节点比较多的话需要写很多代码,这时候就可以使用 @babel/template 包来批量创建。
const template = require('@babel/template').default
const code = template(`
function add(a, b) {
return a + b;
}
`)()
console.log(code)
输出
{
"type": "FunctionDeclaration",
"params": [
{
"type": "Identifier",
"name": "a"
},
{
"type": "Identifier",
"name": "b"
}
],
"generator": false,
"async": false,
"id": {
"type": "Identifier",
"name": "add"
},
"body": {
"type": "BlockStatement",
"directives": [],
"body": [
{
"type": "ReturnStatement",
"argument": {
"type": "BinaryExpression",
"operator": "+",
"left": {
"type": "Identifier",
"name": "a"
},
"right": {
"type": "Identifier",
"name": "b"
}
}
}
]
}
}
https://babeljs.io/docs/babel-template
这个包有这些 api:
template
模板会根据解析结果返回单个语句或语句数组,上面演示过了!
template.smart
这与默认模板 API 相同,根据解析结果返回单个节点或节点数组。(下面是个输出节点数组的例子)
const code = template.smart(`
function add(a, b) {
return a + b;
}
add(1,2)
`)()
console.log(JSON.stringify(code))
输出
[
{
"type": "FunctionDeclaration",
"params": [
{
"type": "Identifier",
"name": "a"
},
{
"type": "Identifier",
"name": "b"
}
],
"generator": false,
"async": false,
"id": {
"type": "Identifier",
"name": "add"
},
"body": {
"type": "BlockStatement",
"directives": [],
"body": [
{
"type": "ReturnStatement",
"argument": {
"type": "BinaryExpression",
"operator": "+",
"left": {
"type": "Identifier",
"name": "a"
},
"right": {
"type": "Identifier",
"name": "b"
}
}
}
]
}
},
{
"type": "ExpressionStatement",
"expression": {
"type": "CallExpression",
"callee": {
"type": "Identifier",
"name": "add"
},
"arguments": [
{
"type": "NumericLiteral",
"value": 1,
"extra": {
"rawValue": 1,
"raw": "1"
}
},
{
"type": "NumericLiteral",
"value": 2,
"extra": {
"rawValue": 2,
"raw": "2"
}
}
]
}
}
]
template.statement
返回单个语句节点,如果结果不是单个语句,则抛出异常。(例如下面输出是
IfStatement)
const template = require('@babel/template').default
const code = template.statement(`
if(a){
console.log(a)
}
`)()
console.log(JSON.stringify(code))
输出
{
"type": "IfStatement",
"test": {
"type": "Identifier",
"name": "a"
},
"consequent": {
"type": "BlockStatement",
"directives": [],
"body": [
{
"type": "ExpressionStatement",
"expression": {
"type": "CallExpression",
"callee": {
"type": "MemberExpression",
"object": {
"type": "Identifier",
"name": "console"
},
"property": {
"type": "Identifier",
"name": "log"
},
"computed": false
},
"arguments": [
{
"type": "Identifier",
"name": "a"
}
]
}
}
]
},
"alternate": null
}
如果不为单个语句
const template = require('@babel/template').default
const code = template.statement(`
if(a){
console.log(a)
}
if(b){
console.log(b)
}
`)()
console.log(JSON.stringify(code))
执行的时候就会抛出异常 Found multiple statements but wanted one
$ node app.js
E:\better\babel_go\node_modules\@babel\template\lib\builder.js:64
throw err;
^
Error: Found multiple statements but wanted one
at E:\better\babel_go\node_modules\@babel\template\lib\formatters.js:35:11
at Object.unwrap (E:\better\babel_go\node_modules\@babel\template\lib\formatters.js:16:14)
template.statements
如其名,返回一个语句节点数组。(上面那个报错的拿这个就OK啦!)
const template = require('@babel/template').default
const code = template.statements(`
if(a){
console.log(a)
}
if(b){
console.log(b)
}
`)()
console.log(JSON.stringify(code))
输出
[
{
"type": "IfStatement",
"test": {
"type": "Identifier",
"name": "a"
},
"consequent": {
"type": "BlockStatement",
"directives": [],
"body": [
{
"type": "ExpressionStatement",
"expression": {
"type": "CallExpression",
"callee": {
"type": "MemberExpression",
"object": {
"type": "Identifier",
"name": "console"
},
"property": {
"type": "Identifier",
"name": "log"
},
"computed": false
},
"arguments": [
{
"type": "Identifier",
"name": "a"
}
]
}
}
]
},
"alternate": null
},
{
"type": "IfStatement",
"test": {
"type": "Identifier",
"name": "b"
},
"consequent": {
"type": "BlockStatement",
"directives": [],
"body": [
{
"type": "ExpressionStatement",
"expression": {
"type": "CallExpression",
"callee": {
"type": "MemberExpression",
"object": {
"type": "Identifier",
"name": "console"
},
"property": {
"type": "Identifier",
"name": "log"
},
"computed": false
},
"arguments": [
{
"type": "Identifier",
"name": "b"
}
]
}
}
]
},
"alternate": null
}
]
template.expression
返回表达式节点的AST
const template = require('@babel/template').default
const code = template.expression(`
a = 1
`)()
console.log(JSON.stringify(code))
输出
{
"type": "AssignmentExpression",
"operator": "=",
"left": {
"type": "Identifier",
"name": "a"
},
"right": {
"type": "NumericLiteral",
"value": 1,
"extra": {
"rawValue": 1,
"raw": "1"
}
},
"extra": {
"parenthesized": true,
"parenStart": 0
}
}
template.program
返回模板的 Program 节点。
const template = require('@babel/template').default
const code = template.program(`
let a = 0
if(a === 0){
a = 1
}else{
a = 2
}
console.log(a)
`)()
console.log(JSON.stringify(code))
输出
{
"type": "Program",
"sourceType": "module",
"interpreter": null,
"directives": [],
"body": [
{
"type": "VariableDeclaration",
"kind": "let",
"declarations": [
{
"type": "VariableDeclarator",
"id": {
"type": "Identifier",
"name": "a"
},
"init": {
"type": "NumericLiteral",
"value": 0,
"extra": {
"rawValue": 0,
"raw": "0"
}
}
}
]
},
{
"type": "IfStatement",
"test": {
"type": "BinaryExpression",
"operator": "===",
"left": {
"type": "Identifier",
"name": "a"
},
"right": {
"type": "NumericLiteral",
"value": 0,
"extra": {
"rawValue": 0,
"raw": "0"
}
}
},
"consequent": {
"type": "BlockStatement",
"directives": [],
"body": [
{
"type": "ExpressionStatement",
"expression": {
"type": "AssignmentExpression",
"operator": "=",
"left": {
"type": "Identifier",
"name": "a"
},
"right": {
"type": "NumericLiteral",
"value": 1,
"extra": {
"rawValue": 1,
"raw": "1"
}
}
}
}
]
},
"alternate": {
"type": "BlockStatement",
"directives": [],
"body": [
{
"type": "ExpressionStatement",
"expression": {
"type": "AssignmentExpression",
"operator": "=",
"left": {
"type": "Identifier",
"name": "a"
},
"right": {
"type": "NumericLiteral",
"value": 2,
"extra": {
"rawValue": 2,
"raw": "2"
}
}
}
}
]
}
},
{
"type": "ExpressionStatement",
"expression": {
"type": "CallExpression",
"callee": {
"type": "MemberExpression",
"object": {
"type": "Identifier",
"name": "console"
},
"property": {
"type": "Identifier",
"name": "log"
},
"computed": false
},
"arguments": [
{
"type": "Identifier",
"name": "a"
}
]
}
}
]
}
使用字符串占位符
const template = require('@babel/template').default
const generator = require("@babel/generator").default
const { identifier,stringLiteral } = require('@babel/types')
const buildRequire = template(`
var IMPORT_NAME = require(SOURCE);
`);
const ast = buildRequire({
IMPORT_NAME: identifier("cunwang"),
SOURCE: stringLiteral("cunwang"),
});
console.log(generator(ast).code)
or 使用这样 %%XXX%%占位符
var %%IMPORT_NAME%% = require(%%SOURCE%%);
这里我们使用 generator 来打印AST 生成的代码,更直观的感受字符串占位符的效果!
var cunwang = require("cunwang");
不使用占位符,使用es6模板字符串代替
刚开始我就在想为什么不能直接使用模板字符串呢?其实是
template这个不支持内部嵌入外部通过模板字符串引入的变量!
const template = require('@babel/template').default
const generator = require('@babel/generator').default
const { identifier, stringLiteral } = require('@babel/types')
const IMPORT_NAME = 'cunwang',
SOURCE = 'cunwang'
const buildRequire = template(`
var ${IMPORT_NAME} = require(${SOURCE});
`)
console.log(generator(buildRequire).code)

如果想使用模板字符串,那种方式更方便 通过简单的方法将字符串解析为 AST,则可以使用 .ast 版本的模板。
const template = require('@babel/template').default
const generator = require('@babel/generator').default
const { identifier, stringLiteral } = require('@babel/types')
const IMPORT_NAME = 'cunwang',
SOURCE = 'cunwang'
const buildRequire = template.ast(`
var ${IMPORT_NAME} = require(${SOURCE});
`)
console.log(generator(buildRequire).code)

这些方法同样也接受一些 options 具体可见文档 https://babeljs.io/docs/babel-template#options
下面是一个保留注释的配置options
const template = require('@babel/template').default
const generator = require('@babel/generator').default
const { identifier, stringLiteral } = require('@babel/types')
const IMPORT_NAME = 'cunwang',
SOURCE = 'cunwang'
const buildRequire = template.ast(
`
// 注释
var ${IMPORT_NAME} = require(${SOURCE});
`,
{
preserveComments: true, // 保留注释
}
)
console.log(generator(buildRequire).code)
输出
Administrator@□□□□ MINGW64 /e/better/babel_go
$ node app.js
// 注释
var cunwang = require(cunwang);
@babel/generator
Turns an AST into code.
这个提供了一些将AST转换为目标代码字符串的能力(上面有使用过)
export default function generate(
ast: t.Node,
opts?: GeneratorOptions,
code?: string | { [filename: string]: string },
): GeneratorResult;
-
第一个参数是要打印的 AST。
-
第二个参数是 options,指定打印的一些细节,比如通过 comments 指定是否包含注释,通过 minified 指定是否包含空白字符。
-
第三个参数当多个文件合并打印的时候需要用到文档
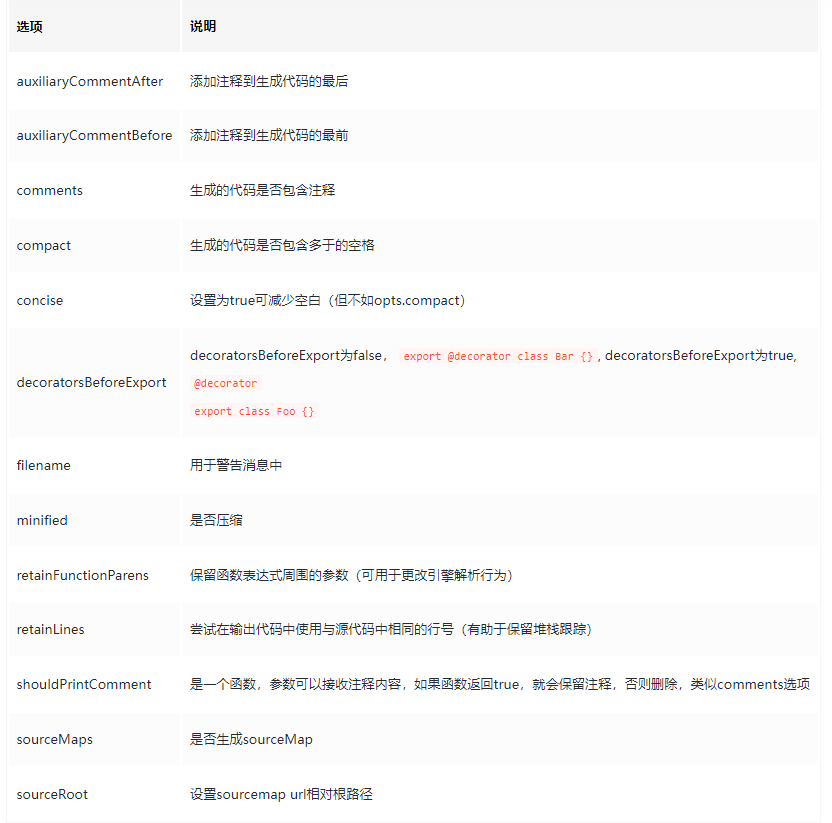
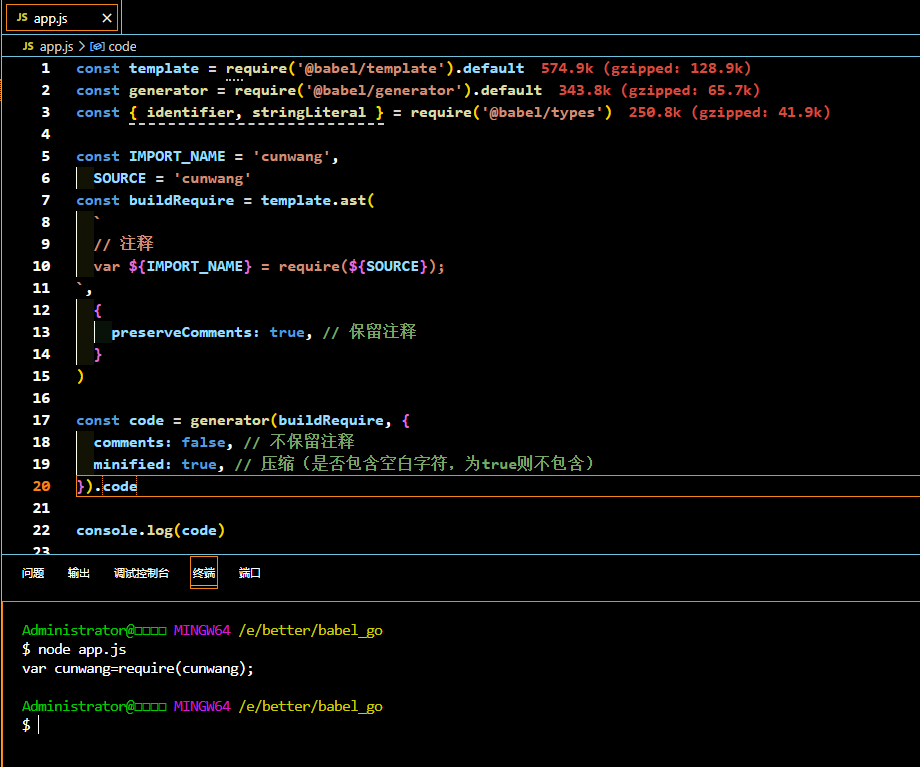
可以看到,虽然转为AST设置了保留注释,但是generator生成code字符串因为配置了不保留注释,所以注释仍然被干掉了~
配置了 minified 代码可以去掉的空白字符也被干掉了!
生成sourcemap
const generate = require('@babel/generator').default
const { parse } = require('@babel/parser')
const a = 'var a = 1;'
const b = 'var b = 2;'
const astA = parse(a, { sourceFilename: 'a.js' })
const astB = parse(b, { sourceFilename: 'b.js' })
const ast = {
type: 'Program',
body: [].concat(astA.program.body, astB.program.body),
}
const { code, map } = generate(
ast,
{ sourceMaps: true },
{
'a.js': a,
'b.js': b,
}
)
console.log(map)
{
version: 3,
file: undefined,
names: [ 'a', 'b' ],
sourceRoot: undefined,
sources: [ 'a.js', 'b.js' ],
sourcesContent: [ 'var a = 1;', 'var b = 2;' ],
mappings: 'AAAA,IAAIA,CAAC,GAAG,CAAC;ACAT,IAAIC,CAAC,GAAG,CAAC'
}
@babel/code-frame
https://babeljs.io/docs/babel-code-frame
babel 的报错一半都会直接打印错误位置的代码,而且还能高亮,
我们打印错误信息的时候也可以用,就是 @babel/code-frame 这个包。
const { codeFrameColumns } = require('@babel/code-frame')
// 原始 code 字符串
const rawLines = `class Foo {
constructor() {
console.log("hello");
}
}`
// 指定位置
const location = {
start: { line: 2, column: 17 },
end: { line: 4, column: 3 },
}
const result = codeFrameColumns(rawLines, location, {
/* options */
highlightCode: true, // 高亮代码
})
console.log(result)
执行效果
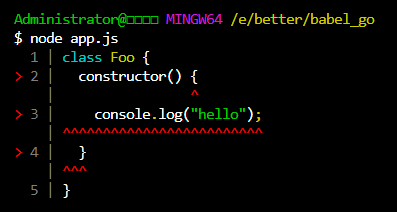
Options
highlightCode |
boolean默认为 false,切换语法高亮显示代码的 JavaScript 终端。 |
|---|---|
linesAbove |
行以上number, defaults to 2. 提示的地方上面展示几行代码(调整在错误上方显示的行数。) |
linesBelow |
number,默认为 3 (调整显示在错误下方的行数。) |
forceColor |
boolean, defaults to false.启用此选项可强制将代码以 JavaScript 语法高亮显示(适用于非终端);覆盖 highlightCode。 |
message |
string, 字符串,否则不显示输入一个字符串,该字符串将在代码中高亮显示的位置旁边内嵌显示(如果可能)。如果无法内嵌显示,则将置于代码框架上方。 |
const { codeFrameColumns } = require('@babel/code-frame')
// 原始 code 字符串
const rawLines = `class Foo {
constructor() {
console.log("hello");
}
}`
// 指定位置
const location = {
start: { line: 2, column: 17 },
end: { line: 4, column: 3 },
}
const result = codeFrameColumns(rawLines, location, {
/* options */
highlightCode: true, // 高亮代码
message: 'Some custome error!',
})
console.log(result)
Administrator@□□□□ MINGW64 /e/better/babel_go
$ node app.js
1 | class Foo {
> 2 | constructor() {
| ^
> 3 | console.log("hello");
| ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
> 4 | }
| ^^^ Some custome error!
5 | }
@babel/core
https://babeljs.io/docs/babel-core
babel 的功能就是通过前面讲的包实现的(@babel/parser、@babel/traverse、@babel/generaotr、@babel/types、@babel/template 等)
babel 基于这些包来实现编译、插件、预设等功能的包就是 @babel/core。完成整个编译流程,从源码到目标代码,生成 sourcemap。实现 plugin 和 preset 的调用。
看一些API,注意下面有一些API的过期提示 例如 babel.transform 这种只能在babel 6 版本使用
In Babel 6, this method was synchronous and
transformSyncdid not exist. For backward-compatibility, this function will behave synchronously if no callback is given. If you’re starting with Babel 7 and need synchronous behavior, please usetransformSyncsince this backward-compatibility will be dropped in Babel 8.在 Babel 6 中,该方法是同步的,而 transformSync 并不存在。为了向后兼容,如果没有给出回调,本函数将同步运行。如果您使用的是 Babel 7,并且需要同步行为,请使用 transformSync,因为这种向后兼容性将在 Babel 8 中取消。
注意:不带 sync、async 的 api 已经被标记过时了,也就是 transformXxx 这些,后续会删掉,不建议用
直接用
transformXxxSync和transformXxxAsync。也就是明确是同步还是异步。
如果用了错误的版本会报错!

@babel/core 支持 plugin 和 preset,一般我们配置的都是对象的格式,其实也有一个 api 来创建,也就是 createConfigItem:
createConfigItem(value, options) // configItem



评论区